
Terminal Velocity of a Falling Sphere in Air
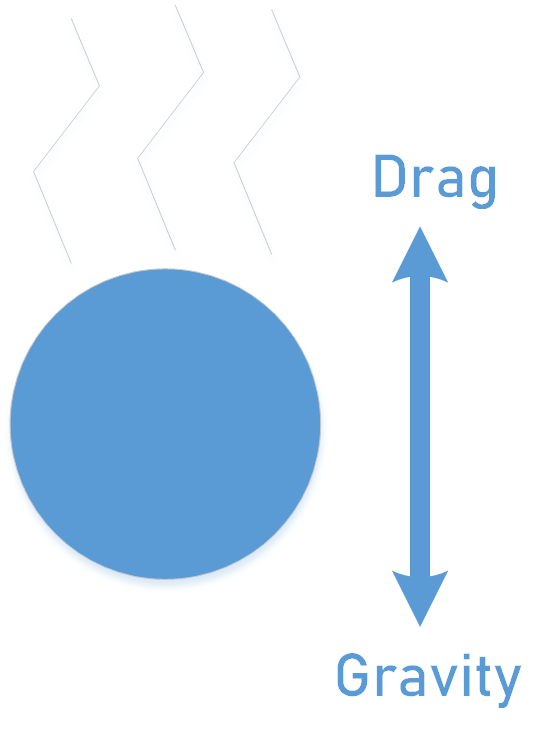
This tool calculates the terminal falling velocity of a spherical object moving in the air with gravity pulling the object downwards. The air resistance (drag force) increases with the increasing acceleration of a falling object under gravity. A velocity is reached where the air resistance balances the gravitational acceleration on the object. As a result, the object moves with a constant velocity thereafter which is called terminal falling velocity.
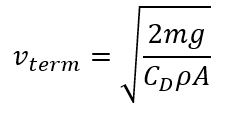
where m in the above equation is the object mass, ρ is the density of air, A is the sphere cross-sectional area, CD is the drag coefficient and g is the gravitational acceleration.
Type the required values to get the terminal velocity:
Sphere Diameter (m)
Sphere Density (ρp, kg/m3)
Air Density (ρair, kg/m3)
Terminal velocity (m/s)
Drag Coefficient
Reynolds Number